The Internet of Things (IoT) isn’t only for connecting the latest gadgets, like a voice-activated speaker or a smart thermostat, to your increasingly connected home.
In fact, the same circumstances that have led to the explosion in smart consumer gadgets, such as universal wireless connectivity, cloud computing, cheap sensors, and better artificial intelligence, are also being used in conjunction with big data to power the next generation of industry, as well.
This new technological layer, called the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), is transforming massive industries like manufacturing, energy, mining, and transportation – and it’ll have a multi-trillion dollar impact on the economy as a whole.
The Birth of the Industrial Internet
Today’s infographic comes to us from Kepware, and it shows how these technological forces have emerged over time to make the IIoT possible.
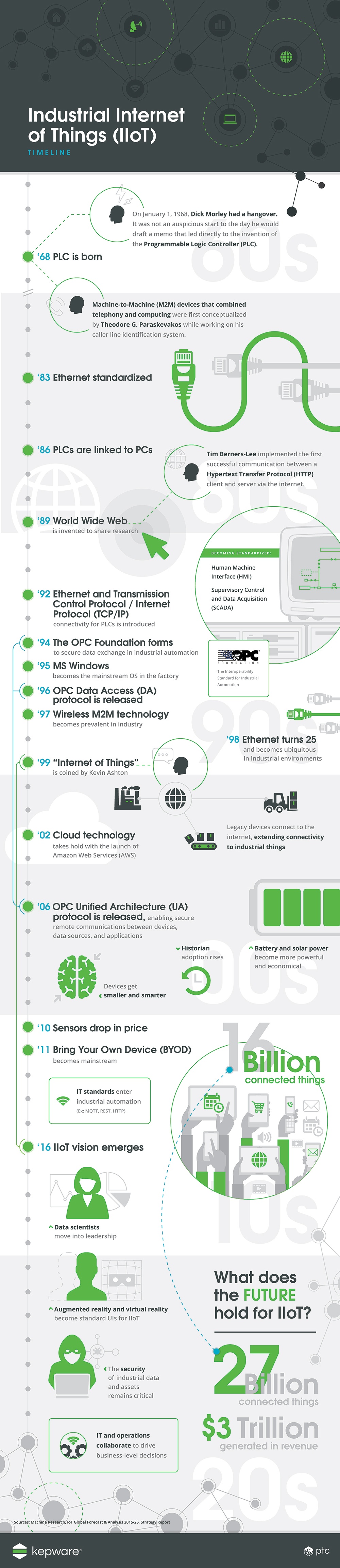
The road to the creation of the IIoT started in 1968, when engineer Dick Morley made one of the most important breakthroughs in manufacturing history.
That year, Morley and a group of geek friends invented the programmable logic controller (PLC), which would eventually become irreplaceable in automating assembly lines and industrial robots in factories.
Other Major Innovations
Here are some other major innovations that were instrumental in making the IIoT possible:
1983: Ethernet is standardized
1989: Tim Berners-Lee creates Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
1992: TCP/IP allows PLCs to have connectivity
2002: Amazon Web Services launches, and cloud computing starts to take hold
2006: OPC Unified Architecture (UA) enables secure communications between devices, data sources, and applications.
2006: Devices start getting smaller, and batteries and solar energy are becoming powerful and more economical.
2010: Sensors drop in price, enabling them to be put into pretty much everything
And today, the IIoT is a big deal: it’s transforming the backbone of major industries by adding a new layer of technology that helps companies optimize operations, track and analyze equipment, implement predictive maintenance, make sense of massive amounts of data, and make real-time decisions that were never before possible.
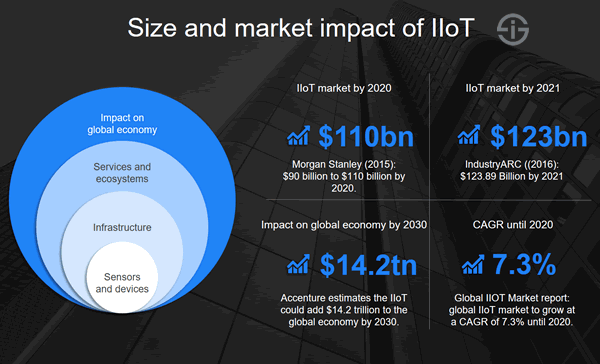
And by 2030, the IIoT is estimated by Accenture to have a $14.2 trillion on the global economy – making it one of the most important forces shaping the future business world today.