The Briefing
- The U.S. share of the global economy has nearly halved since 1960
- America’s nominal GDP in current U.S. dollars is $21.4 trillion, or about 24% of the share of the global economy
The World’s Largest Economy
The U.S. is the world’s largest economy by nominal GDP, and its influence on the global economy is quite remarkable.
As of 2019, the U.S. made up almost a quarter of the global economy. But how has America’s share of the economic pie changed over time?
The U.S. Share of the Global Economy Over Time
While the U.S. economy has grown quickly over time, the global economy has grown quicker.
Since peaking at 40% in 1960, the U.S. share of the world economy has been cut almost in half, despite a rising national GDP and being the birthplace of some of the biggest companies on the planet.
| Year | Global GDP | U.S. GDP | U.S. Share of Global Economy |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1960 | $1.37T | $0.53T | 40% |
| 1965 | $1.97T | $0.74T | 38% |
| 1970 | $2.96T | $1.07T | 36% |
| 1975 | $5.92T | $1.69T | 28% |
| 1980 | $11.23T | $2.86T | 25% |
| 1985 | $12.79T | $4.34T | 34% |
| 1990 | $22.63T | $5.96T | 26% |
| 1995 | $30.89T | $7.64T | 25% |
| 2000 | $33.62T | $10.25T | 30% |
| 2005 | $47.53T | $13.04T | 28% |
| 2010 | $66.13T | $14.99T | 23% |
| 2015 | $75.22T | $18.23T | 24% |
| 2019 | $87.80T | $21.43T | 24% |
The decline of America’s contribution to global GDP has been slow and uneven, with crests and troughs along the way.
Between 1965 and 1980, the country’s share fell by 13 percentage points, mainly due to stagflation of the 1970s. This decline was followed by Reaganomics and a period of strong recovery, which helped propel the U.S. share of the global economy back up to 34% by 1985.
The whipsawing would continue. Between 1985 and 1995, the U.S share fell by another 11 percentage points, only to bounce back to a local peak of 30% by the year 2000.
Downhill From Here?
Since the beginning of the 21st century, growth in many developing markets has continued at a rapid pace—and the U.S. share of the global economy has decreased as a result.
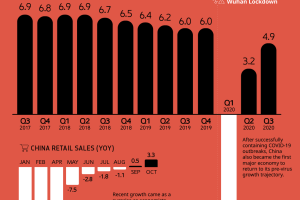
Until 2005, the U.S. still accounted for 28% of global GDP, but the Global Financial Crisis left a big dent, and its share fell to 23% by 2010. It has since remained relatively stable at 24%.
It’s important to put this decline into perspective. For instance, China’s share of the global economy grew from 4% in 1960 to 16.3% in 2019. Over that same time period, other countries like South Korea, Brazil, Mexico, Indonesia, and India also saw their emergence on the economic world stage, as well.
What the Future Holds
The COVID-19 pandemic has changed the course of the global economy, with most countries experiencing a recession in 2020. America’s economic position will depend on how quickly it can recover compared to the rest of the world.
Where does this data come from?
Source: The World Bank
Details: Data is in current U.S. dollars. Dollar figures for GDP are converted from domestic currencies using single year official exchange rates.