The Anatomy of a Smart City
There is no doubt that the city will be the defining feature of human geography for the 21st century.
Globally, there are 1.3 million people moving to cities each week – and by 2040, a staggering 65% of the world’s population will live in cities.
At the same time, the 600 biggest urban areas already account for 60% of global GDP, and this will only rise higher as cities become larger and more prosperous. In fact, experts estimate that up to 80% of future economic growth in developing regions will occur in cities alone.
The Smart City: A Necessary Step
As cities become an even more important driver of the global economy and wealth, it’s becoming crucial to ensure that they are optimized to maximize efficiency and sustainability, while enhancing the quality of life in each urban conglomeration.
Today’s infographic from Postscapes helps define the need for smart cities, and it also gives great examples of how technology can be applied in urban settings to facilitate cities that work better for their citizens.
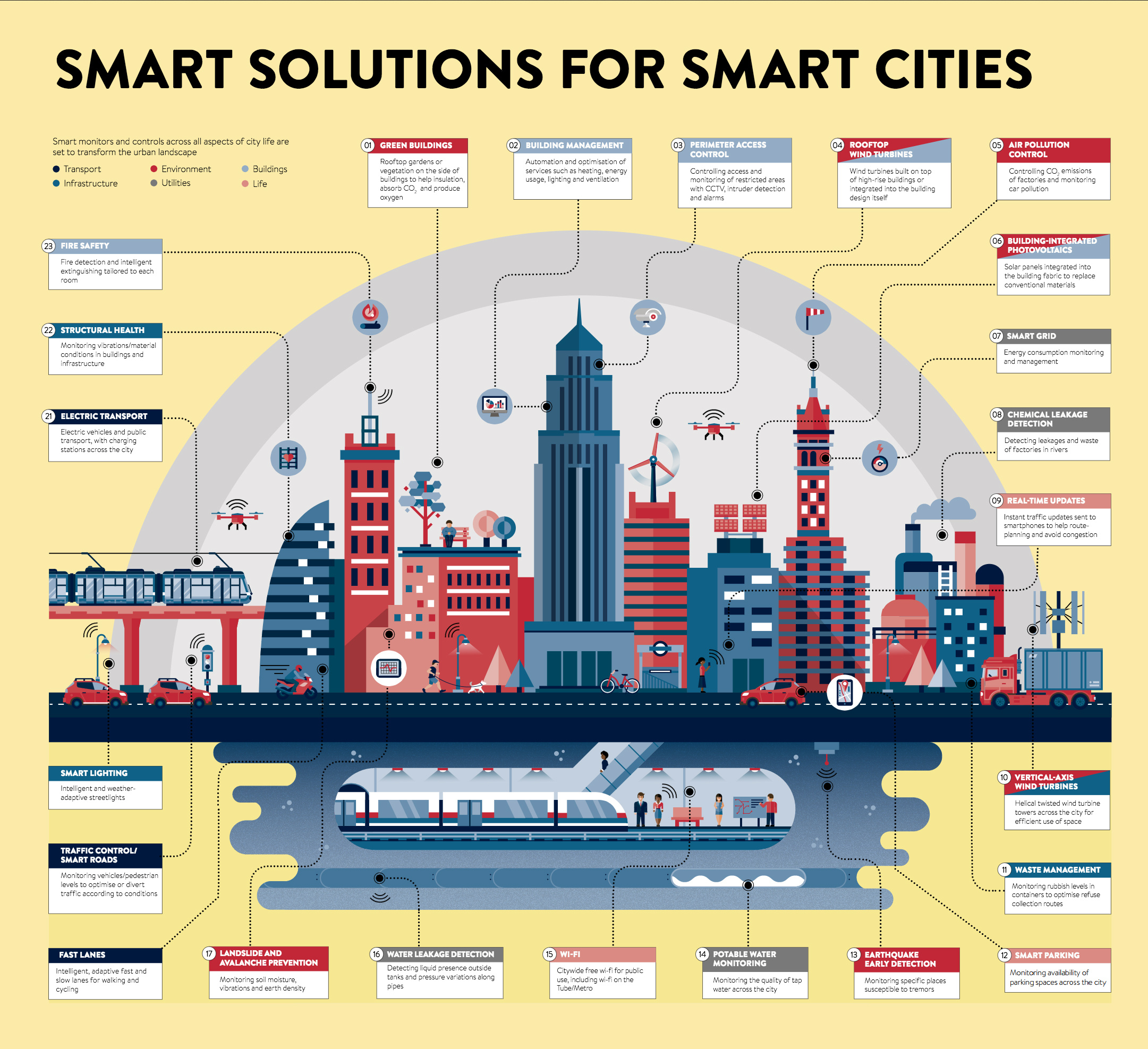
Features of Tomorrow’s Cities
Smart cities will use low power sensors, wireless networks, and mobile-based applications to measure and optimize everything within cities.
Here are just some examples: (click below image to open full-size version)
Smart city solutions will fall into six broad categories, transforming the urban landscape:
1. Infrastructure
Smart lighting is one of the most important solutions that will be implemented in citywide infrastructure. While smart lighting sounds trivial at first glance, it’s worth noting that lighting alone consumes a whopping 19% of the world’s total electricity.
2. Buildings
Heating, energy usage, lighting, and ventilation will be managed and optimized by technology. Solar panels will be integrated into building design, replacing traditional materials. Fire detection and extinguishing is tailored to individual rooms.
3. Utilities
Smart grids (used for energy consumption monitoring and management), water leakage detection, and water potability monitoring are just some smart city aspects on the utilities side.
4. Transport
Intelligent, adaptive fast lanes and slow lanes (cycling, walking) will be implemented, while charging stations through the city will power EVs.
5. Environment
Air pollution control, renewable energy, and waste management solutions will make for greener cities. Rooftop gardens or side vegetation will be integrated into building designs, to help with insulation, provide oxygen, and absorb CO2.
6. Life
There will be citywide Wi-Fi for public use, while real-time updates will provide citizens information on traffic congestion, parking spaces, and other city amenities.
The Effect?
Cisco estimates that smarter cities will have impressive increases in efficiency: using many of the above concepts, cities can improve energy efficiency by 30% in 20 years.
Simultaneously, it’s estimated that the broad market for smart cities products and services will be worth $2.57 trillion by 2025, growing at a clip of 18.4% per year on average.